Wave Properties and Information |
Pace: 10 class periods
|
Purpose of Unit and IB Connections
|
Key Concept:
Relationship |
Related Concept:
Energy Patterns Models |
Global Context:
Scientific and technical innovation |
Conceptual Understanding:
Wave energy is found in a variety of relationships used in creative expression. |
Statement of Inquiry:
Information moves based on a pattern of energy changes. |
Pretest and Differentiation
If you score a 90% or above on this pretest on your first attempt you will not need to complete any of the practice for this unit and an accelerated assignment will be provided. The pretest is not open internet or buddy or book. This pretest will be timed and may only be completed in class.
Part 1: Parts of a Wave
Outline
|
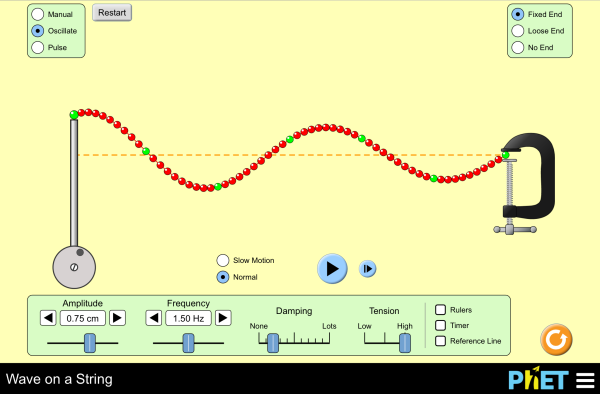
Wave properties need to be visible to students to promote understanding. Use tuning forks, rope springs, and slinkies to model waves and their properties!
Materials Required: Slinkies (1 per group) Rope Springs (1 per group) Beaker or shallow dish (1 per group) Tuning Fork (2 of different sizes per group) |
Parts of a Wave Essential Question and Skills
| ||||||
11-12 May
#1 Cornell Notes: Ch9.1 Harmonic Motion
#2 Cornell Notes and Self Quiz: Wave Period
#3 Parts of a Wave Practice Page
|
#1 Cornell Notes: Ch9.1 Harmonic Motion (pgs 218-223)
|
Key Terms:
| ||||||||||||
|
#2 Cornell Notes and Self Quiz: Wave Period
|
| ||||||
15-16 May
#4 Parts of a Wave EdPuzzle
#5 Parts of a Wave Game
#6 Parts of a Wave Mastery Check
|
#4 Parts of a Wave EdPuzzle
|
|
Optional Deep Dive
| |||||||
Part 2: Sound Waves
16-17 May
#7 CN and Self Quiz: What are Sound Waves?
#8 CN Book: Ch9.3: Sound
#9 How Sound Works Game and CN
|
#7 VIDEO NOTES
Add to your Cornell Notes using What are Sound Waves? from study.com Add details and diagrams to your notes. Complete the quiz. Scores below an 80% should review anything missed, add to your notes and retake the quiz. Record your BEST SCORE on the top of #7 #8 BOOK NOTES: Chapter 9: Section 3 (pgs 232-238) Use the key terms, your text and the notes below to complete Cornell Notes for this section. Include diagrams and examples as much as possible.
|
#8 Key Terms
| ||||||||||||||
#9 How Sound Works
Complete the HOW SOUND WORKS FLASH NOTES (won't work on iPhones/iPads) and complete with a partner. No need to complete notes unless you choose to.
Complete the HOW SOUND WORKS FLASH NOTES (won't work on iPhones/iPads) and complete with a partner. No need to complete notes unless you choose to.
19-22 May
#10 Sound Waves Practice Page
#11 Sound Waves LAB
#12 Sound and Waves Mastery Check
#10 Sound Waves Practice Page
Complete "The nature of Sound Waves" practice below. Check your answer HERE after you have completed
Complete "The nature of Sound Waves" practice below. Check your answer HERE after you have completed
| sound_waves_practice.pdf | |
| File Size: | 77 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
SKIP AND DO NOT COMPLETE THIS LAB
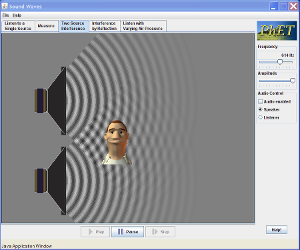
#11 Sound Waves LAB Complete the Sound Wave Lab using the PhET simulator to the right with a partner. Each student is responsible for completing their own lab and turning it in
| |||||||
#12 Sound and Waves Mastery Check
- Complete the Mastery Check on our Google Classroom.
Electromagnetic Radiation Part 1
22 May
#13 VIDEO CN and Self Quiz: Transverse Waves
#14 BOOK CN: Chapter 9: Section 2 (pgs 225-230)
#15 Waves Flash Notes
#16 Interference Practice Page
#13 VIDEO NOTES and Self Quiz: Transverse Waves
2. Add to your Cornell Notes using Transverse Wave: Definition, Parts & Examples from study.com Add details and diagrams to your notes. Complete the quiz. Scores below an 80% should review anything missed, add to your notes and retake the quiz. Record your BEST SCORE on the top of the page
2. Add to your Cornell Notes using Transverse Wave: Definition, Parts & Examples from study.com Add details and diagrams to your notes. Complete the quiz. Scores below an 80% should review anything missed, add to your notes and retake the quiz. Record your BEST SCORE on the top of the page
|
#14 BOOK NOTES: Chapter 9: Section 2 (pgs 225-230)
Use the key terms, your text and the notes below to complete Cornell Notes for this section. Include diagrams and examples as much as possible.
#15 Practice Complete the WAVES FLASH NOTES (won't work on iPhones/iPads). No need to complete notes unless you choose to. #16 Interference Practice Page Complete "Inference of Waves" practice below. Check your answer HERE after you have completed. |
Ch 9.2 Key Terms
| ||||||||||||
| interference.pdf | |
| File Size: | 78 kb |
| File Type: | |
23 May
#17 Exam Review Packet
25-26 May
Electromagnetic Radiation Part 2
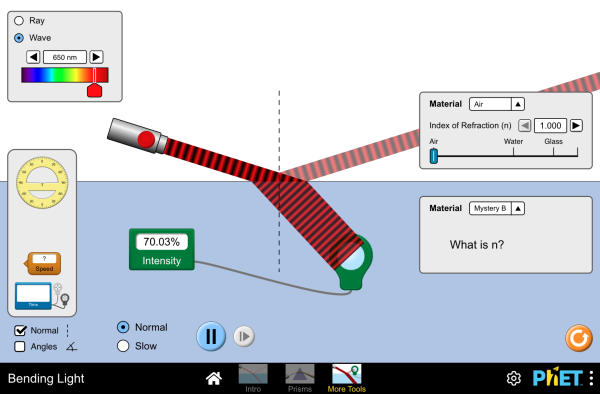
The path that light travels can be traced as straight lines, except at surfaces between different transparent materials (e.g., air and water, air and glass) where the light path bends. (MS-PS4-2)
|
#18 Bending Light Lab
| |||||||
|
#19 EdPuzzle: What are Electromagnetic Waves?
|
|
26-2 June
Electromagnetic Radiation Part 3
|
#20 VIDEO NOTES AND #20 BOOK NOTES: Chapter 10: Section 1 (pgs 246-252)
|
#20 Terms to Know
| ||||||||||||||
| light1.pdf | |
| File Size: | 74 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
#22 VIDEO NOTES Transmission of Light
|
#23 Ch10.3 Key Terms
| ||||||||||||||
|
#24 Reflection, Refraction, Scatter and Absorption
#25 Light Mastery Check
|
#24 Reflection, Refraction, Scatter and Absorption GAME
|
Binder Check Rubric and WAVES POST TEST
- Complete the Post Test on our Google Classroom
DEEP DIVE
Molecules and Light LAB
Complete the Sound Wave Lab using the PhET simulator below with a partner. Each student is responsible for completing their own lab and turning it for extra credit by Friday, 3 June.
Molecules and Light LAB
Complete the Sound Wave Lab using the PhET simulator below with a partner. Each student is responsible for completing their own lab and turning it for extra credit by Friday, 3 June.
| molecules_and_light_guided_inquiry_studenthandout.pdf | |
| File Size: | 506 kb |
| File Type: | |
Website incomplete after this point
Electromagnetic Radiation Part 4
Outline |
SY 2015-16 |
Information Technologies and Instrumentation
|
1. Introduction to Matter and Energy
|
#10 LABS
Part 1: Complete the Slinky Lab with a partner Part 2: Watch the Labs with your partner. Complete the quiz. Scores below an 80% should review anything missed, add to your notes and retake the quiz. Record your Quiz Grades on the TOP of your #7. Diffraction & Interference: Physics Lab Reflection & Refraction of Light
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||