Electric Circuits
|
Essential Questions
Current Electricity — Circuits
|
Standards Covered
P4.10C Given diagrams of many different possible connections of electric circuit elements, identify complete circuits, open circuits, and short circuits and explain the reasons for the classification. P4.10D Discriminate between voltage, resistance, and current as they apply to an electric circuit. P3.7A |
18-19 January
|
Standard Practiced:
P4.10C Terms to Know: Electric Charge Static Electricity Electric Current Ampere Volts |
|
#1 EDpuzzle: What is Electric Current? (20 min)
USING ELECTRICITY GAME (15 min)
Part 1: Using what you learned in the game and self quiz. Draw a Electric Circuit Diagram that represents how Electric Current moves.
#3 Mastery Check: Electric Current in the GCR (10 min) |
| ||||||||||||
22 January
|
Standard Practiced:
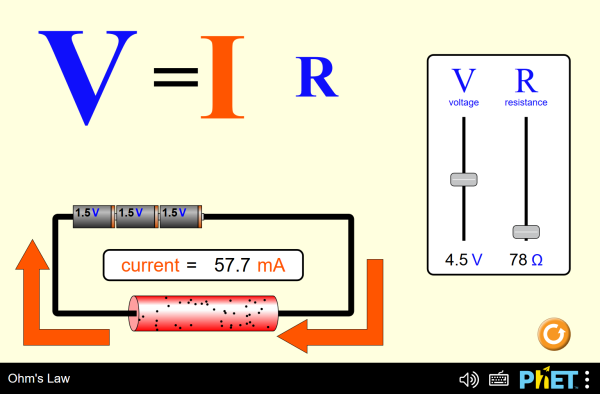
P4.10A Terms to Know: electric circuit resistance ohm Ohm's Law conductor insulator Big Ideas:
1. The resistance of a wire depends on the conductivity of the material used in the wire and also on the thickness and length of the wire. 2. Ohm's law states that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage impressed across the circuit, and is inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit. |
#4 8.2 Electric Circuits and Power BOOK Cornell Notes (~15 min)
- Review Chapter 8 section 2 below.
- Complete 8.2 Electric Circuits and Power Cornell Notes for this section including the "terms to know".
- Include diagrams and examples when possible.
|
| ||||||||||||
|
#5 Voltage, Current and Resistance Practice (~25 min)
|
| ||||||
23 January
|
Standard Practiced:
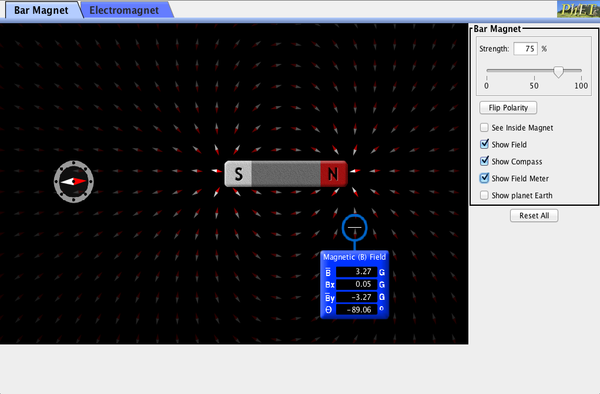
P3.7A Terms to Know: Magnetic Forces Magnetic Pole Permanent Magnetic Big Ideas:
1. All magnetic forces are the result of moving electrons. 2. Similar poles always repel each other, and opposite poles always attract. |
#6 Learning Electricity and Circuits Practice
- Complete Learning Electricity and Circuits Practice sheet using the online module. Be ready to review as a class.
| electricity_and_circuits_ws.pdf | |
| File Size: | 234 kb |
| File Type: | |
#7 GAME and PRACTICE
CHANGING CIRCUITS SIMULATION (5-10 min)
CHANGING CIRCUITS SIMULATION (5-10 min)
- PLAY THIS GAME and explore how we can manipulate electricity to do work There is not practice page to go along with this.
- PLAY THIS GAME and explore how we can manipulate electricity to do work There is not practice page to go along with this.
24 January
#8 Electric Circuit and Current Practice
#9 Mastery Check: Electric Current and Circuits
#8 Electric Circuit and Current Practice (15 min)
- Complete the practice on your own or with your table partner
- Check your answers with the KEY in class and fix misunderstandings if needed.
| #8 Electric Circuit and Current Practice.pdf | |
| File Size: | 73 kb |
| File Type: | |
#9 Mastery Check: Electric Current and Circuits in the GCR
25- 29 January
Exam Practice Test and Study Guide Review
1 February
#10 Cornell Notes: Properties of Magnets
|
Review Chapter 8 section 3 (pages 203-210) below or during class.
|
TERMS TO KNOW (pages 203-210)
| ||||||
|
Standard Practiced:
P4.10C Terms to Know: electric power Big Idea:
How can you express electric power in terms of current and voltage? |
1 February
| ||||||
| electromagnets_and_ohms_law_lab.docx | |
| File Size: | 28 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
|
Optional on your own
| ||||||||
| #12 electricty_and_magnetism_video.pdf | |
| File Size: | 163 kb |
| File Type: | |
#13 EDpuzzle Circuit Review: Cornell Notes (20 min)
|
2 February
| ||||||||
| electricty_lab.pdf | |
| File Size: | 2082 kb |
| File Type: | |
#15 Mastery Check in the GCR
5-6 February
#16 Electrical Circuit Inquiry Labs 1-4
#17 Directions
- Complete the following labs with materials in the classroom and THIS lab sheet.
- Turn into the box when completed.
|
Lab 1
Materials:
|
Lab 2
Materials:
|
|
Lab 3
Materials:
1. Connect the battery and two flashlight bulbs so that both bulbs are lit. Include a schematic diagram of each set up with labels. 2. Add another flashlight bulb in series with the other two bulbs. Draw and label all parts of the circuit. Does the brightness of the light bulbs change? Why or why not? 3. Replace one of the light bulbs with a burned-out light bulb. What happens to the other lights in the circuit? 4. Determine if this is an example of a series circuit or a parallel circuit. Explain your answer. 5. Check your results with another person from a different group. 6. Share your recorded lab results in your notebook with your teacher. |
Lab 4
Materials:
|
OPTIONAL AT HOME LAB
3 February
Circuit Lab
Online Circuit Construction PhET
|
Complete the simulation using the guided inquiry document below. You will use what you learn in the practice labs at the bottom.
|
Click below to get started | ||||||
7 February
#17 Post Lab Mastery Check in GCR
#17 Post Lab Mastery Check in GCR
- Based on your lab 3-4 work what is the difference between series and parallel circuits? How did you come up with an answer to the question?
- What might be examples of items that use electricity that are on a series circuit? How are you sure?
- What might be examples of items that use electricity that are on a parallel circuit? How are you sure?
Optional Deep Dive
Review
|
Student created example
| ||||||
Remediation, Late Work and Extra Credit within 10
days of test date or by the end of the trimester
days of test date or by the end of the trimester