Energy Part 2
|
Pace: 5 class periods
|
|
BIG IDEAS
P4.2 Energy Transformations Energy is often transformed from one form to another. The amount of energy before a transformation is equal to the amount of energy after the transformation. In most energy transformations, some energy is converted to thermal energy. |
Standards Covered:
P4.2A Account for and represent energy transfer and transformation in complex processes (interactions). P4.2B Name devices that transform specific types of energy into other types (e.g., a device that transforms electricity into motion). P4.2C Explain how energy is conserved in common systems (e.g., light incident on a transparent material, light incident on a leaf, mechanical energy in a collision). P4.2D Explain why all the stored energy in gasoline does not transform to mechanical energy of a vehicle. |
9 Pretest and DifferentiationIf you score a 90% or above on this pretest on your first attempt you will not need to complete any of the practice for this unit and an accelerated assignment will be provided. The pretest is not open internet or buddy or book. This pretest will be timed and may only be completed in class.
|
Chapter 9 PDF Textbook and Notes
| ||||||||||||
9.1 Work
15 December
p 145-146
|
Big Idea: Work is done when a force acts on an object and the object moves in the direction of the force
|
Standard(s):
P4.2A |
|
BOOK NOTES:
1. Use the key terms and your text to complete Cornell Notes for this section. Include diagrams and examples as much as possible. VIDEO NOTES
2. Add to your 9.1 Cornell Notes using the online learning module from Education Portal, Work: Define and Math (expires 11 January). Complete the quiz and record in your notebook. PRACTICE 1 Complete the Practice sheet below, pages are provided in class. Glue in your lab notebook after you have checked your answers. Skip #5 and #7.
PRACTICE 2
Explain why the statement in the picture to the right is true in your lab notebook. |
Terms to Know:
-impulse -work -Formula: W=Fd -joule
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ||||||
9.2 Power
16 December
pg 146-147
|
Big Idea: Power equals the amount of work done divided by the time interval during which the work is done
|
Standard(s):
P4.2A |
|
BOOK and VIDEO NOTES:
1. Use the key terms and your text to complete Cornell Notes for this section. Include diagrams and examples as much as possible. VIDEO NOTES o your 9.2 Cornell Notes using the online learning module from Education Portal, Power: Define and Math (expires 11 January). Complete the quiz and record in your notebook. PRACTICE Complete the Practice sheet below, pages are provided in class. Glue in your lab notebook after you have checked your answers.
|
Terms to Know:
-power -Formula: power=work done/time interval -watt | ||||||
9.3 Mechanical Energy
pg 147
17 December
|
Big Idea: The two forms of mechanical energy are kinetic and potential
|
Standard(s):
P4.2A P4.2C |
|
BOOK NOTES:
1. Use the key terms and your text to complete Cornell Notes for this section. Include diagrams and examples as much as possible. VIDEO NOTES:
2. Add to your 9.3 Cornell Notes using the online learning module from Education Portal, Mechanical Energy (expires 11 January). Complete the quiz and record in your notebook. PRACTICE: 3. Explain in your notebook how mechanical energy is conserved during a car crash? |
Terms to know:
-energy -mechanical energy |
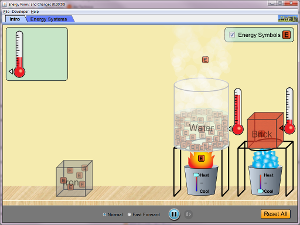
Practical Energy Transfers
18-19 December
|
Big Idea: Name devices that transform specific types of energy into other types (e.g., a device that transforms electricity into motion).
|
Standard(s):
P4.2B |
|
PRACTICE
Voice Thread or other (20-30 min) Create a voice thread reviewing the energy transfer in any example in the PhET simulation below. Use the video example as a guide as to what you will create. Be sure to include: a. all energy types identified in your voice or text b. all transfer of energy (change of energy from one form to anther) identified in your voice or text c. digitally share with teacher upon completion |