Chapter 27: Light and Electromagnetic Waves |
Pace: 8 class periods
Checkpoint: 17 March |
|
Essential Questions:
|
Standards Covered:
|
Kahoot and DifferentiationPre and Post test data will be collected and used by the teacher to offer alternative projects to demonstrate mastery. You may also self select for an alternative assignment upon conferencing with your teacher. Please talk to your teacher if you have any questions.
Student Examples: |
Chapter 27 PDF textbook and notes
| ||||||||||||||
27.1 Early Concepts of Light
| |||||||
| cpps1401.pdf | |
| File Size: | 138 kb |
| File Type: | |
Standard Practiced:
prior knowledge
Big Ideas:
-Light has a dual nature, part particle and part wave.
-The speed of light has been calculated to about 300,000 km/s.
Terms/Names to know:
Photons
Olaus Roemer
Christian Huygens
Albert Michelson
Speed of light
Light-year
prior knowledge
Big Ideas:
-Light has a dual nature, part particle and part wave.
-The speed of light has been calculated to about 300,000 km/s.
Terms/Names to know:
Photons
Olaus Roemer
Christian Huygens
Albert Michelson
Speed of light
Light-year
27.3: Electromagnetic Waves
10 March
|
BOOK NOTES
10-15 min 1. Review Chapter 27 sections 3 and complete Cornell Notes notes for this section including the "terms to know". Include diagrams and examples when possible. VIDEO NOTES 10-15 min 2. Add to your Cornell Notes using Electromagnetic Waves: Definition, Sources & Properties, from Education Portal (expires 2 April). Add details and diagrams to your notes. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM ONLINE MODULE PRACTICE WS 15-30 min 3. Using the online learning module and tools from the National Science Foundation, explore the *Electromagnetic Spectrum learning module. This module should take some time to explore and complete the practice. Complete the practice sheet and check in when completed. Exploration 3 is extra credit.
MASTERY CHECK
5-10 min 4. Electromagnetic waves originate from the vibrations of pure energy and can travel in a vacuum or thru matter. Mechanical Waves originate from the vibrations matter and can only travel thru matter. Explain why radio waves can travel through space, but sound waves cannot. |
Standard(s) Practiced:
P4.6A P4.6B Big Idea: The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radio waves, microwaves, infrared, light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma rays and originate from the vibrations of pure energy. Terms to Know Electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Infrared Ultraviolet | ||||||
27.4: Light and Transparent Materials
27.5: Opaque Materials
11-12 March
|
BOOK NOTES
10-15 min 1. Review Chapter 27 sections 4 and 5 and complete Cornell Notes notes for this section including the "terms to know". Include diagrams and examples when possible. VIDEO NOTES 10-15 min 2. Add to your Cornell Notes using Transparent and Opaque Materials in Electromagnetic Waves, from Education Portal (expires 2 April). Add details and diagrams to your notes. PRACTICE 5-10 min Review the Opaque, Translucent and Transparent Introduction video. Create your own example of each in your lab notebook, screencast or voice thread. REVIEW GAME
5-10 min Play the Transparent, Opaque, and Translucent Game. The game is basic but a good review of the big ideas for this section. MASTERY CHECK 5-10 min How do the transparency and opacity of objects depends on how light waves interact with the materials of those objects. Provide an example for one transparent object and one opaque object. |
Standard(s) Practiced:
P4.9A P4.9B Big Idea: -Light passes through materials whose atoms absorb the energy and immediately reemit it as light. -In opaque materials, any coordinated vibrations given by light to the atoms and molecules are turned into random kinetic energy. Terms to Know: Transparent Opaque Reflection Absorption Remission |
27.Time Delays and Sound Waves
|
Standard(s) Practiced:
P4.6C P4.6D Big Idea: Radio waves travel at the speed of light, 300,000 km/sec. Terms to Know: Radio Wave |
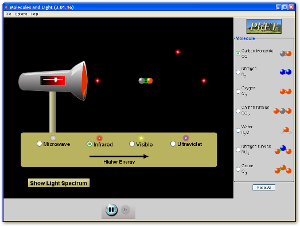
27.Lab
| |||||||||||||
| molecules.light.phetlab.docx | |
| File Size: | 2664 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
If the lab above does not open try opening this file below.
| molecules-and-light_en-1.jar | |
| File Size: | 1232 kb |
| File Type: | jar |
Standard(s) Practiced:
P4.9B
Big Idea:
Identify that absorption of light depends on the molecule and the type of light
Terms to know:
Molecules
Light
Photons
Absorption
P4.9B
Big Idea:
Identify that absorption of light depends on the molecule and the type of light
Terms to know:
Molecules
Light
Photons
Absorption
27.Review
Ignore any review about Polarization and Shadows
|
27 Optional Extra CreditComplete the practice on blue "ASSESS" pages 548-549 #1-17, and 24-32
Complete either of the following practice pages before the Unit Mastery Check for 2 points EXTRA CREDIT on your Post Test.
skip #3, 12, 13, and 14 on the practice assessment of you choose to complete
| ||||||||||||
Remediation, Late Work and Extra Credit due within 10
days of test date.
days of test date.